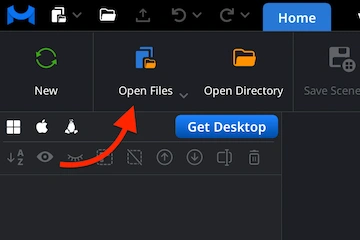
Step 1. Opening CSVs
Start by launching the MeshInspector program. Under the ‘Home’ tab, all import actions begin. To prepare for the conversion from CSV file to ASC, click ‘Open Files.’
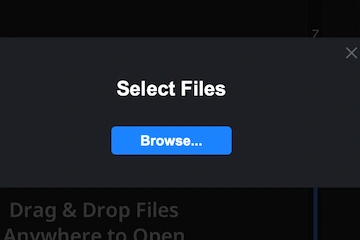
Step 2. Browsing CSVs
The MeshInspector program for 3D data handling will display a small dialog titled ’Select Files.’ Click ’Browse’ button to open your file picker and locate your dataset.
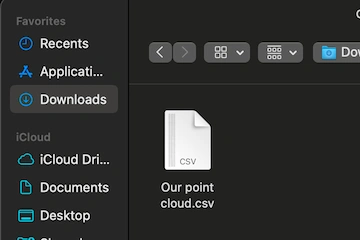
Step 3. Uploading CSVs
Navigate to the folder with your dataset. Select the CSV file. You can double-click the file to confirm your selection or click the ‘Upload’ button once the file is highlighted.
Step 4. Viewing CSVs as Point Clouds
Once the CSV file is uploaded, your point cloud appears in the viewport. It is also listed in our ‘Scene Tree.’ You can explore it using standard navigation controls, e.g., rotate the view by dragging with the left mouse button or using a one-finger touchpad gesture. Panning is available through holding the right mouse button or sliding two fingers. Zoom with the mouse wheel or a pinch gesture. Finally, tilt the perspective by holding Ctrl while dragging with the left mouse button.
Step 5. Exporting CSVs to ACS
With your point cloud selected in the ‘Scene Tree,’ go to the ‘Home’ tab and click ‘Export.’ This command allows you to convert the loaded dataset into another supported format, which includes the ASC format required for this workflow.
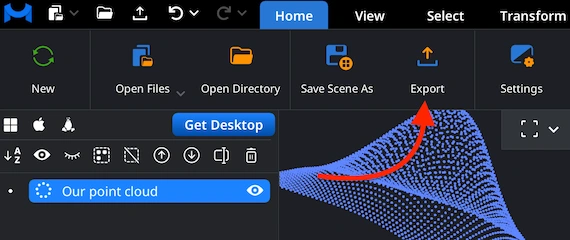
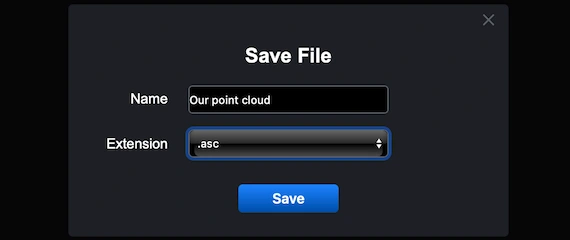
Step 6. Choosing ASC Format
After clicking ‘Export,’ MeshInspector opens a ’Save File’ dialog. Enter a name for your output, then open the’Extension’ dropdown and select .asc from the list of available formats. When everything is set, click ’Save’ to complete the conversion.
Step 7. Assessing ASC Files
Load the ASC file back into the MeshInspector program for 3D data to verify that the dataset has been preserved in a proper fashion. Check that your point clouds appear in our Viewport as coherent 3D structures. Rotate, pan, and zoom ACSs using the navigation controls described above to ensure the geometry behaves naturally and that no axes were unintentionally swapped. The cloud should not appear stretched or oriented in an unexpected direction.
Step 8. Optimizing ASC Files
With your ASC selected in our ‘Scene Tree,’ switch to the ’Points’ tab to access tools for point-based datasets. Locate the’Optimize’ button to click it. This step will remove empty gaps in the memory layout of the point cloud and reorder elements. Thus, spatially close points will be stored in nearby memory locations. While it does not modify the visual structure of the dataset, it helps improve efficiency and prepares the ASC file for smoother processing in downstream workflows.
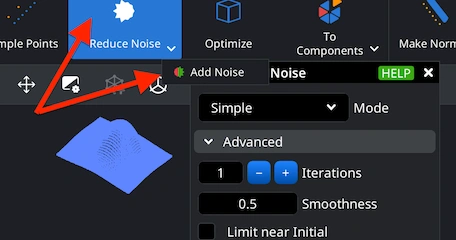
Step 9. Handling Noise Issues
Under the ‘Points’ tab, MeshInspector provides tools for adding and reducing noise in your datasets. For that, click 'Reduce Noise.' Alternatively, you can use the small arrow, located next to it, to select 'Add Noise.' This will opens the dedicated panel. Inside it, you are free to adjust parameters, including mode, iterations, and smoothness to control how noise is applied to the point cloud. When you are ready to commit the changes, click 'Apply' to finalize the operation.