Opening a GCODE file
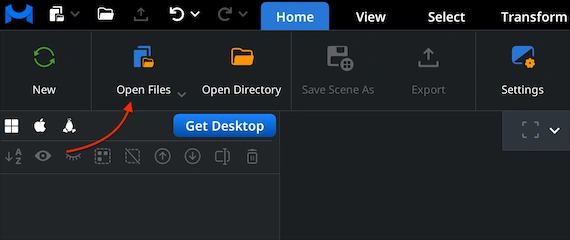
Under the ’Home’ tab, click ’Open Files.’ This option lets you load your GCODE file into MeshInspector for inspection. After you select the file, our viewer imports the full toolpath and prepares it for visualization, regardless of how dense the extrusion data is or how many layers the print contains.
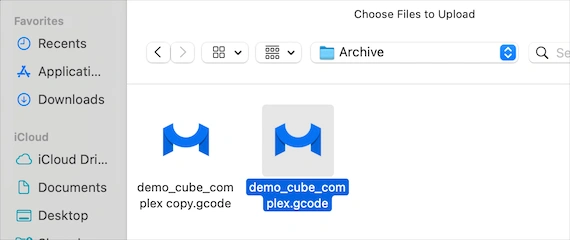
Selecting a GCODE file
Click ’Browse.’ After that, navigate to the folder where your NC file is stored. Then either double-click the file or confirm the selection with Upload. The MeshInspector program for reading NC files can also open entire folders containing multiple operations, which is useful when a workflow is split into components.
Viewing a GCODE File
After the GCODE file is loaded, its toolpath appears. You are free to examine it from any angle. Rotate the GCODE view by dragging with the left mouse button or using a one-finger touchpad gesture. Pan the scene by holding the right mouse button or sliding two fingers on a touchpad. Zoom in or out with the mouse wheel or a pinch gesture. To tilt the view, hold Ctrl and drag with the left mouse button. These controls, taken together, allow you to review layer transitions, extrusion paths, travel lines, and overall print geometry.
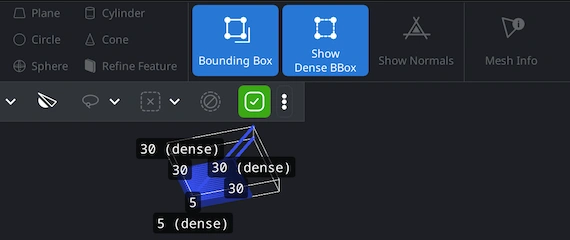
Checking Object Dimensions
Under the ’Inspect’ tab, you can press ’Bounding Box’ or ’Show Dense Box’ to view the physical dimensions of your toolpath. ‘Bounding Box’ displays an axis-aligned box that encloses the selected object. It gives you a quick and clean understanding of your model’s outer limits. ‘Show Dense Box’ reveals the minimal bounding box that tightly wraps the object. This easily accessible option is useful when the print contains angled geometry, overhangs, or tilted paths.
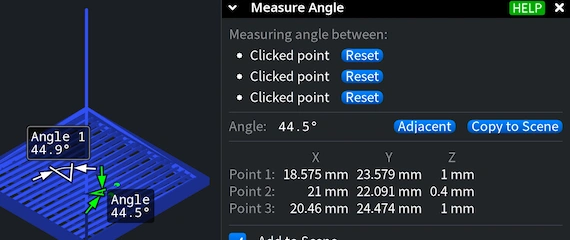
Measuring Angles
MeshInspector allows you to inspect individual features of a GCODE toolpath with precision. To measure an angle, open the ’Measure Angle’ tool from the ’Inspect’ tab. Click three points directly on the toolpath. As soon as you place the third point, the MeshInspector program to read GCODE files quickly calculates the angle and displays it both in the viewport and in the measurement panel, which is convenient when you need to double-check and validate anything of importance to you.
Aligning a GCODE Model with 3-2-1 Align
The ‘3-2-1 Align’ under ‘Transform’ tool makes it possible for users to position their GCODE models precisely within the coordinate system. This method is commonly used in 3D workflows to define a stable orientation based on three reference steps: a primary plane (3 points), a secondary direction (2 points), and a final axis constraint (1 point). In MeshInspector, this workflow allows you to correct toolpaths that were exported in an unexpected orientation or to prepare them for comparison, analysis, or downstream processing.